
Databases power nearly every modern application — and when they slow down, everything slows down. Laggy dashboards, delayed APIs, frustrated users — we’ve all been there.
Whether you’re a backend developer, an aspiring data engineer, or simply someone looking to make their app feel faster and more responsive, this guide is for you. I’ll walk you through 10 real-world strategies to help your database run smoother, respond faster, and scale smarter.
And because optimization isn’t just about quick wins, I’ve included 2 bonus tips to help you keep things running smoothly over time.
Let’s get into it.
🔍 1. Use Indexes to Find Data Faster
Indexes are like road signs for your queries. Without them, the database must scan every row — painfully slow. Add indexes to columns frequently used in WHERE, JOIN, or ORDER BY clauses to instantly improve lookup speed.
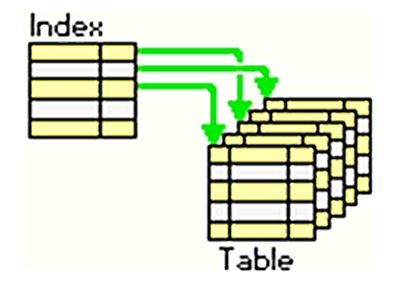
✅ Pro tip: Use
EXPLAINto check whether your query uses indexes or is scanning the full table.
2. Write Smarter Queries, Not Just More
Messy SQL leads to sluggish performance. Avoid SELECT *, filter early, and make joins intentional. Use LIMIT where possible and always profile your queries.
✅ Pro tip: Tools like
EXPLAIN ANALYZE(PostgreSQL) show how your query behaves under the hood.
🏗️ 3. Design a Clean Schema with the Right Data Types
Good performance starts with good design. Normalize your schema to eliminate redundancy — but don’t fear controlled denormalization for read-heavy use cases. Choose tight data types: use INT over VARCHAR when appropriate.
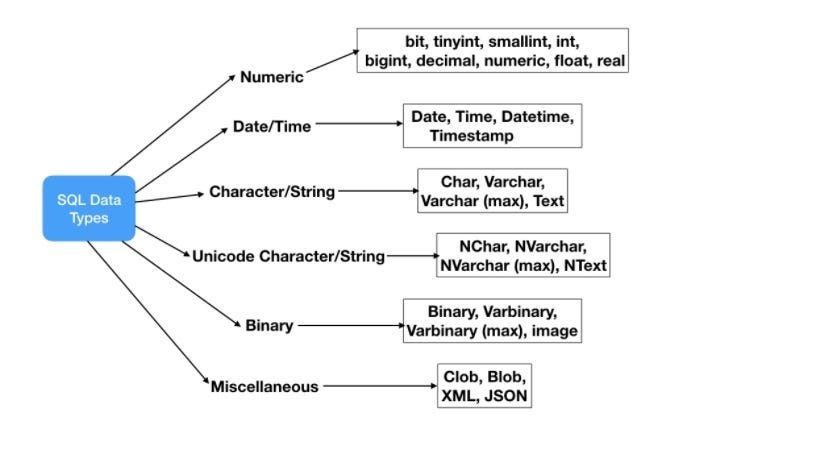
✅ Pro tip: Avoid large text fields unless necessary. Consider UUIDs vs. serial IDs based on scale.
⚡ 4. Speed Up with In-Memory Caching
If your app keeps asking for the same data, use caching. Tools like Redis or Memcached store results in memory, letting you return data faster than any query could.
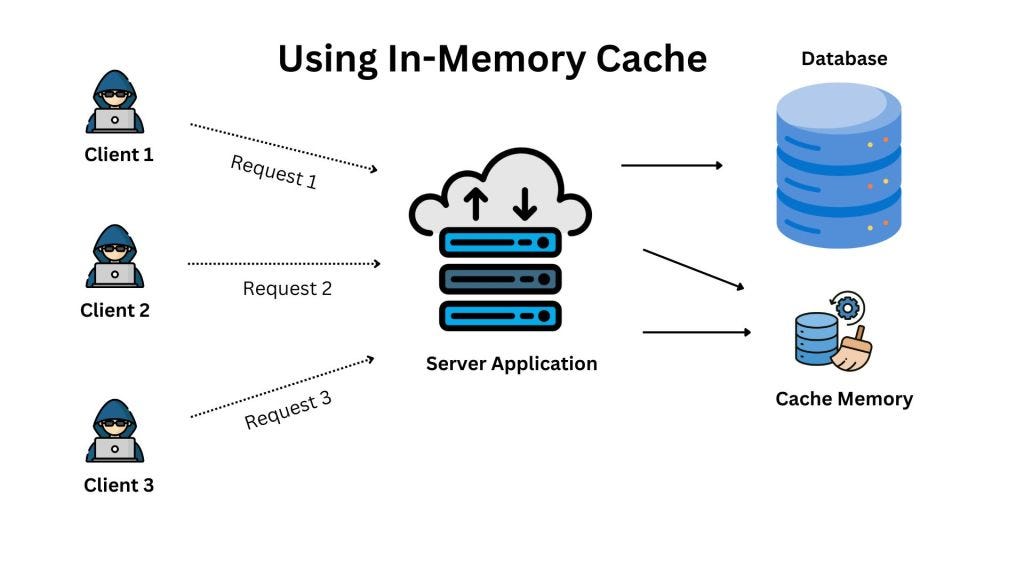
✅ Pro tip: Cache expensive, read-heavy queries with long TTLs. Bust the cache when updates happen.
🧮 5. Precompute Results with Materialized Views
For queries that take forever — especially analytics and reporting — materialized views let you store precomputed results and refresh them periodically.
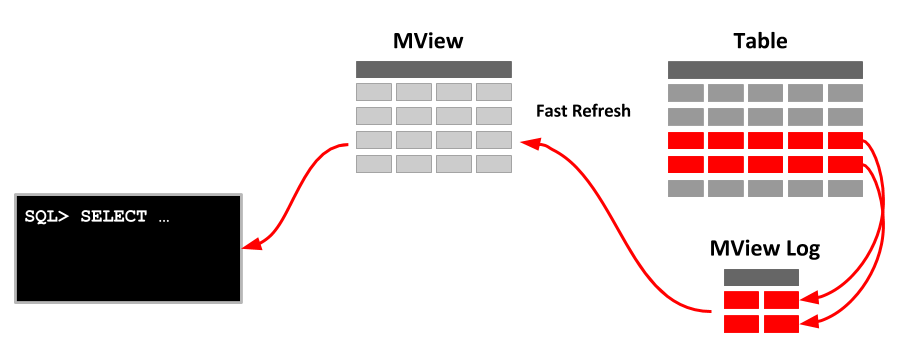
✅ Use case: Monthly reports, dashboards, or any query that aggregates large data sets.
🔄 6. Save Time with Connection Reuse
Constantly opening and closing database connections is expensive. Connection pooling keeps connections open and reuses them across sessions.
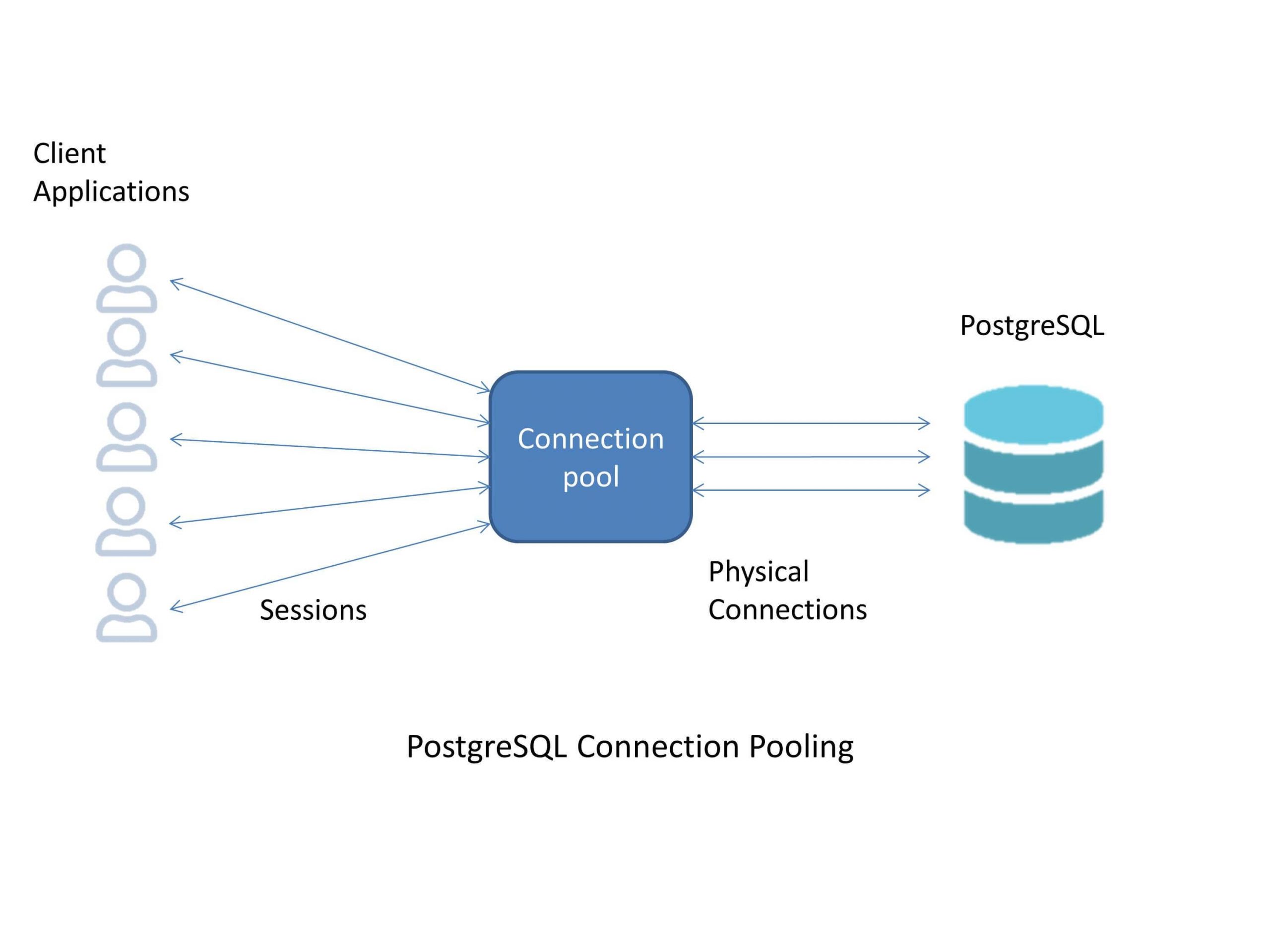
✅ Pro tip: Use built-in pooling features in your ORM or tools like PgBouncer for PostgreSQL.
📚 7. Distribute Reads with Replication
Replication lets you copy data from a primary database to one or more replicas. You can route read queries to replicas, reducing load on the main database and improving availability.
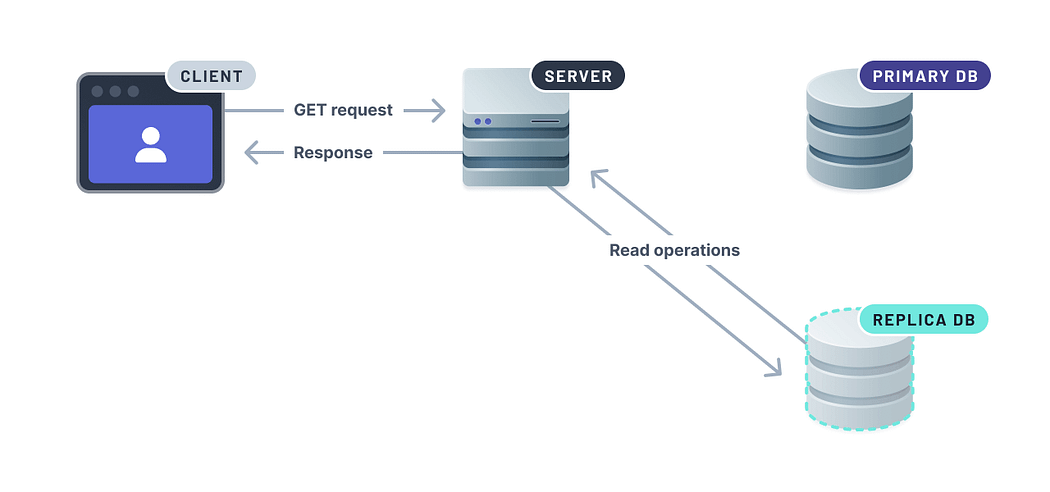
✅ Bonus: Replication also serves as a hot standby for disaster recovery.
📦 8. Divide Large Tables into Smaller Parts
Partitioning splits large tables into manageable chunks (e.g., by date or region). Queries then scan only relevant partitions, not the entire table.
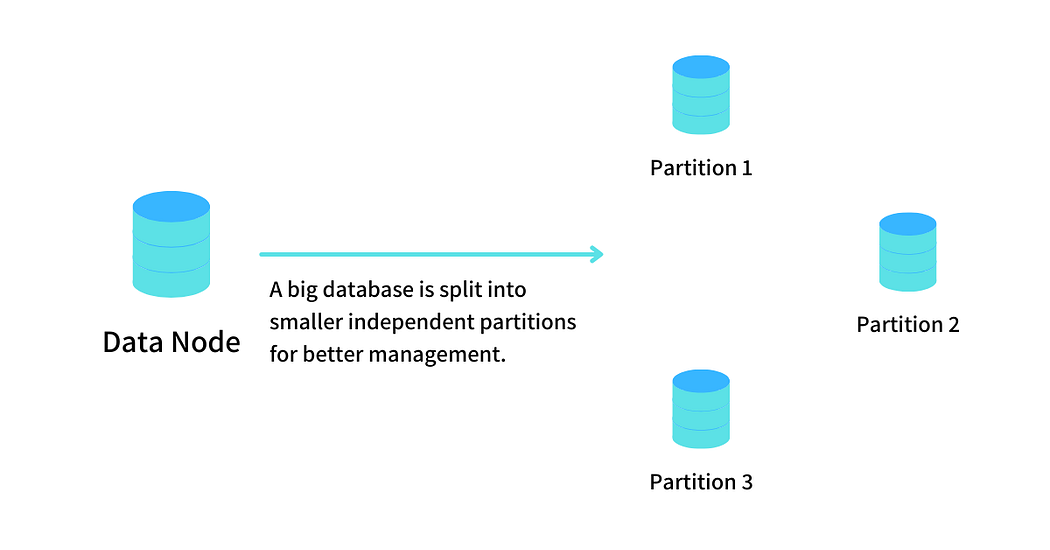
✅ Pro tip: Use range partitioning for time-series data; list partitioning for categorical data.
🗂️ 9. Scale Out with Database Sharding
When one database instance isn’t enough, sharding splits your data horizontally across multiple servers. Each “shard” handles part of the dataset — great for very large applications.
✅ Pro tip: Use a consistent sharding key and plan for cross-shard operations early.
🧹 10. Archive Old Data to Keep Things Lean
Your database doesn’t need to carry a decade of logs. Archive unused or historical data into cold storage or separate archive tables.

✅ Pro tip: Automate archiving with scheduled jobs. Set thresholds by date, size, or status.
🔧 Bonus Section: Keep It Healthy
Even the best-optimized database needs care. These aren’t core strategies, but they’re essential for long-term performance.
👀 11. Watch What Your Database Is Doing
Use monitoring tools like pg_stat_statements, Datadog, or New Relic to spot slow queries, connection issues, and CPU/memory pressure.

✅ Golden rule: Monitor BEFORE users complain — not after.
🛠️ 12. Tune It Regularly, Like a Car
Routine maintenance tasks — vacuuming (for PostgreSQL), reindexing, analyzing table stats — help your database perform consistently as data grows.

✅ Pro tip: Automate these tasks via cron jobs or internal schedulers.
🎯 Wrapping Up
You don’t need to apply all 10 strategies at once. Start with query optimization, indexing, and monitoring. Add caching or replication as your app scales. Only reach for partitioning or sharding when you truly need them.
Database optimization isn’t a one-time fix — it’s an ongoing process. Even small improvements can make a big impact on speed, reliability, and user experience.
💡 Found this guide helpful? Tap the 👏 button to show some love and follow for more insightful blogs and updates.
Thanks for reading — and happy coding! 🚀💚